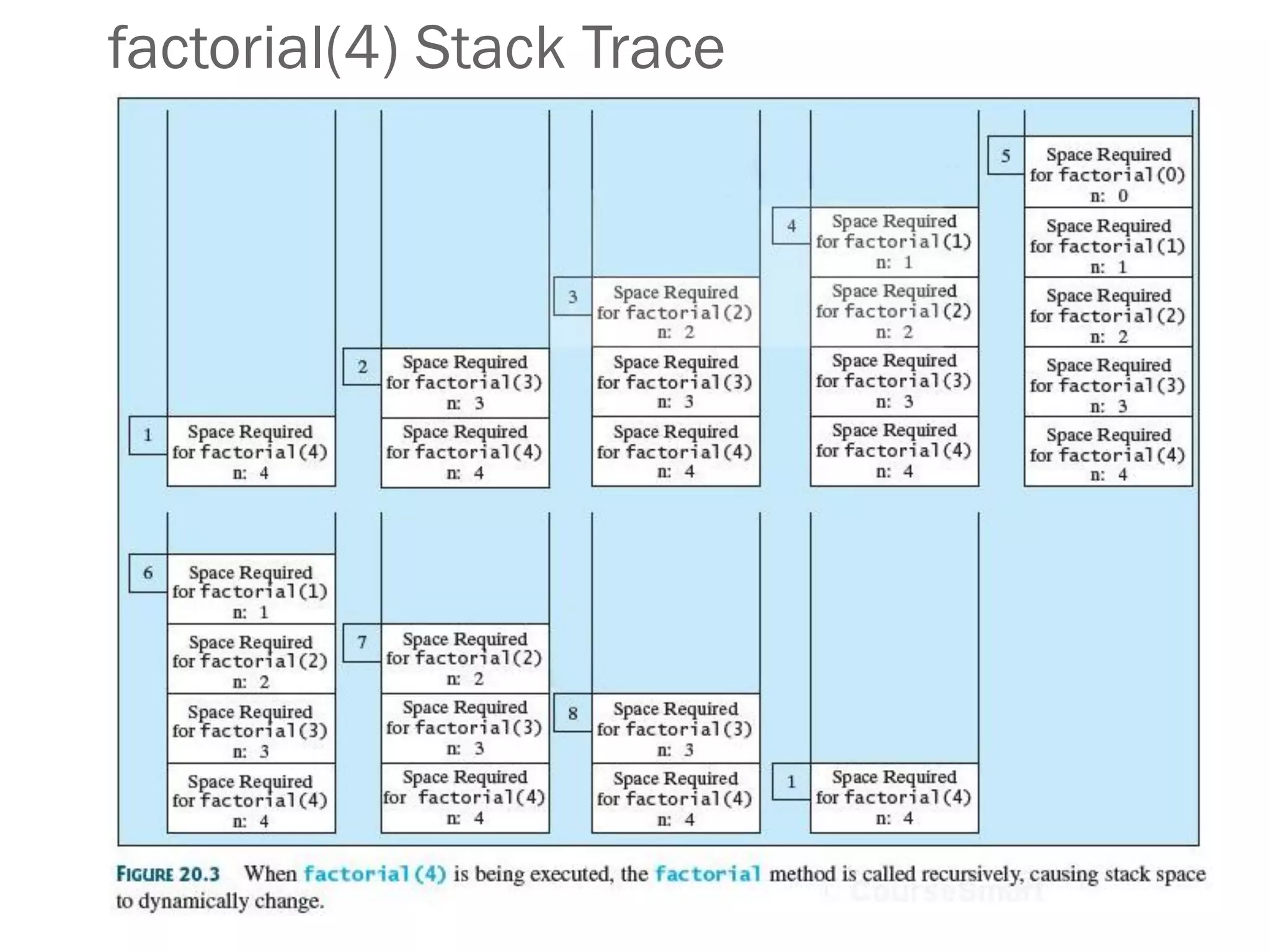
Recursion is a technique for solving complex problems by breaking them down into smaller subproblems. It involves defining a problem in terms of simpler instances of the same problem. Some key examples of using recursion to solve problems include computing factorials, calculating sums, generating Fibonacci numbers, and traversing directory structures. Recursion uses repetition with abstraction - defining functions that call themselves on smaller inputs until they arrive at a base case.


















![Directory Size
20
public class DirectorySize {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.print("Enter a file or a directory: ");
java.util.Scanner input = new java.util.Scanner(System.in);
String s = input.nextLine();
try {
System.out.println( directorySize( new File(s) ) );
}
catch (IOException ex) {
System.out.println(ex.toString());
}
}
public static long directorySize(File file) throws java.io.FileNotFoundException{
if (!file.exists())
throw new java.io.FileNotFoundException(file + " not found");
if (file.isFile()) {
return file.length();
}
else {
File[] files = file.listFiles();
long size = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < files.length; i++)
size += directorySize(files[i]);
return size;
}
}
}](https://crownmelresort.com/image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture5-recursion-150222111835-conversion-gate02/75/Recursion-Computer-Algorithms-20-2048.jpg)




![Solution to Towers of Hanoi
25
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 4;
// moving disks from A to B using C as auxiliary tower
System.out.println("Towers of Hanoi. The moves are:");
moveDisks(n, 'A', 'B', 'C');
}
private static void moveDisks( int n, char fromTower, char toTower, char auxTower) {
if (n == 1)
System.out.println("Move disk " + n + " from "
+ fromTower + " to " + toTower);
else {
moveDisks(n-1, fromTower, auxTower, toTower);
System.out.println("Move disk " + n + " from "
+ fromTower + " to " + toTower);
moveDisks(n-1, auxTower, toTower, fromTower);
}](https://crownmelresort.com/image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture5-recursion-150222111835-conversion-gate02/75/Recursion-Computer-Algorithms-25-2048.jpg)









![Eight Queens
35
0
4
7
5
2
6
1
3
queens[0]
queens[1]
queens[2]
queens[3]
queens[4]
queens[5]
queens[6]
queens[7]](https://crownmelresort.com/image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture5-recursion-150222111835-conversion-gate02/75/Recursion-Computer-Algorithms-35-2048.jpg)

![Eight Queens
37
// start by calling: search(0);
// search for a solution starting on specified row
private static boolean search(int row){
if (row == SIZE)
return true;
for (int column=0; column < SIZE; column++){
queens[row] = column; //place a queen at row,column
if (isValid(row, column) && search(row+1)){
System.out.println("Queen at: " + row + " : " + column);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}//search
// check if a queen can be placed at row i and column j
private static boolean isValid(int row, int column){
for(int i=1; i<= row; i++){
if ( queens[row-i] == column //check column
|| queens[row-i] == column - i //check upleft diagonal
|| queens[row-i] == column + i )//check upright diagonal
return false;
}
return true;
}//isValid](https://crownmelresort.com/image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture5-recursion-150222111835-conversion-gate02/75/Recursion-Computer-Algorithms-37-2048.jpg)