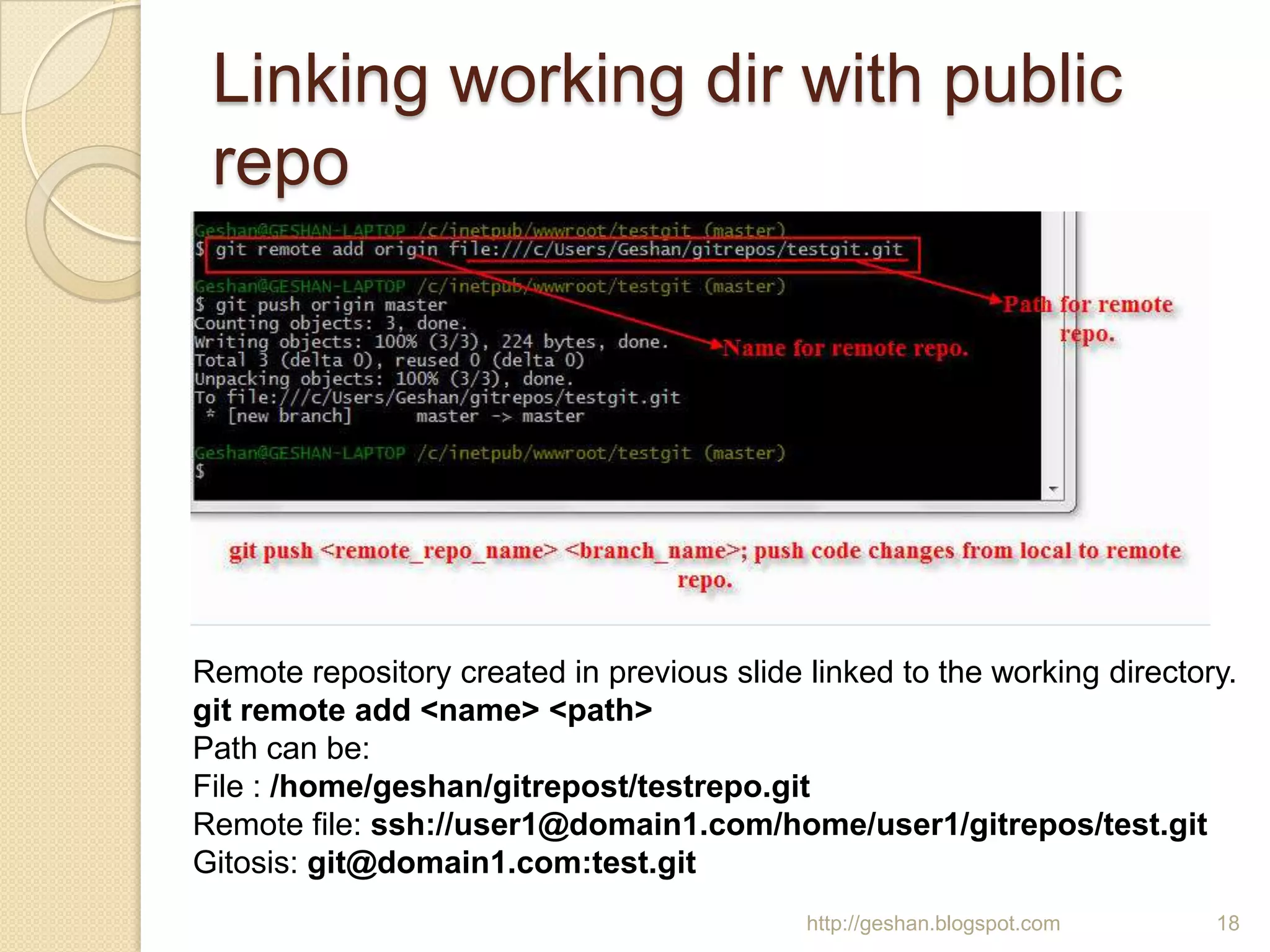
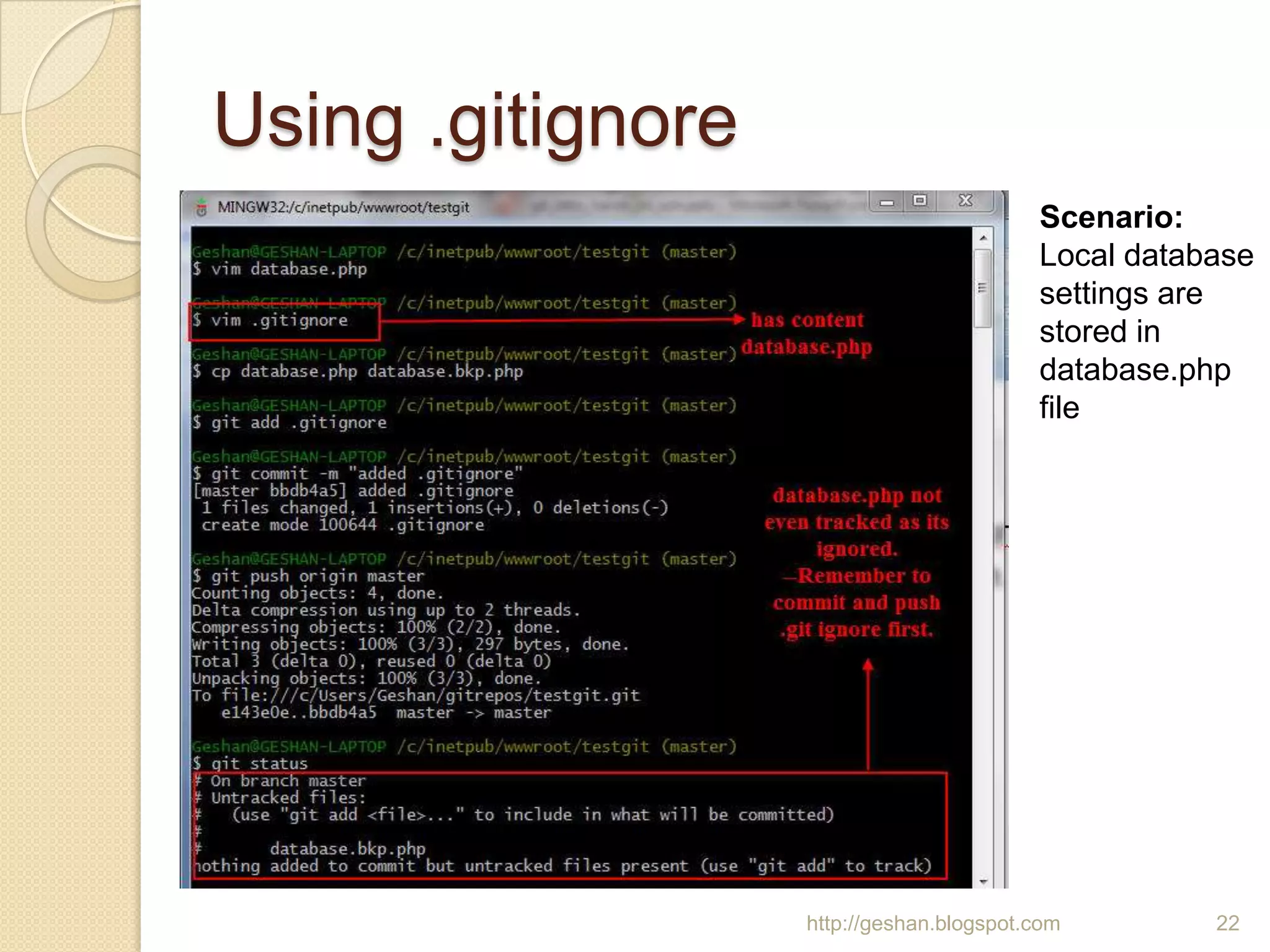
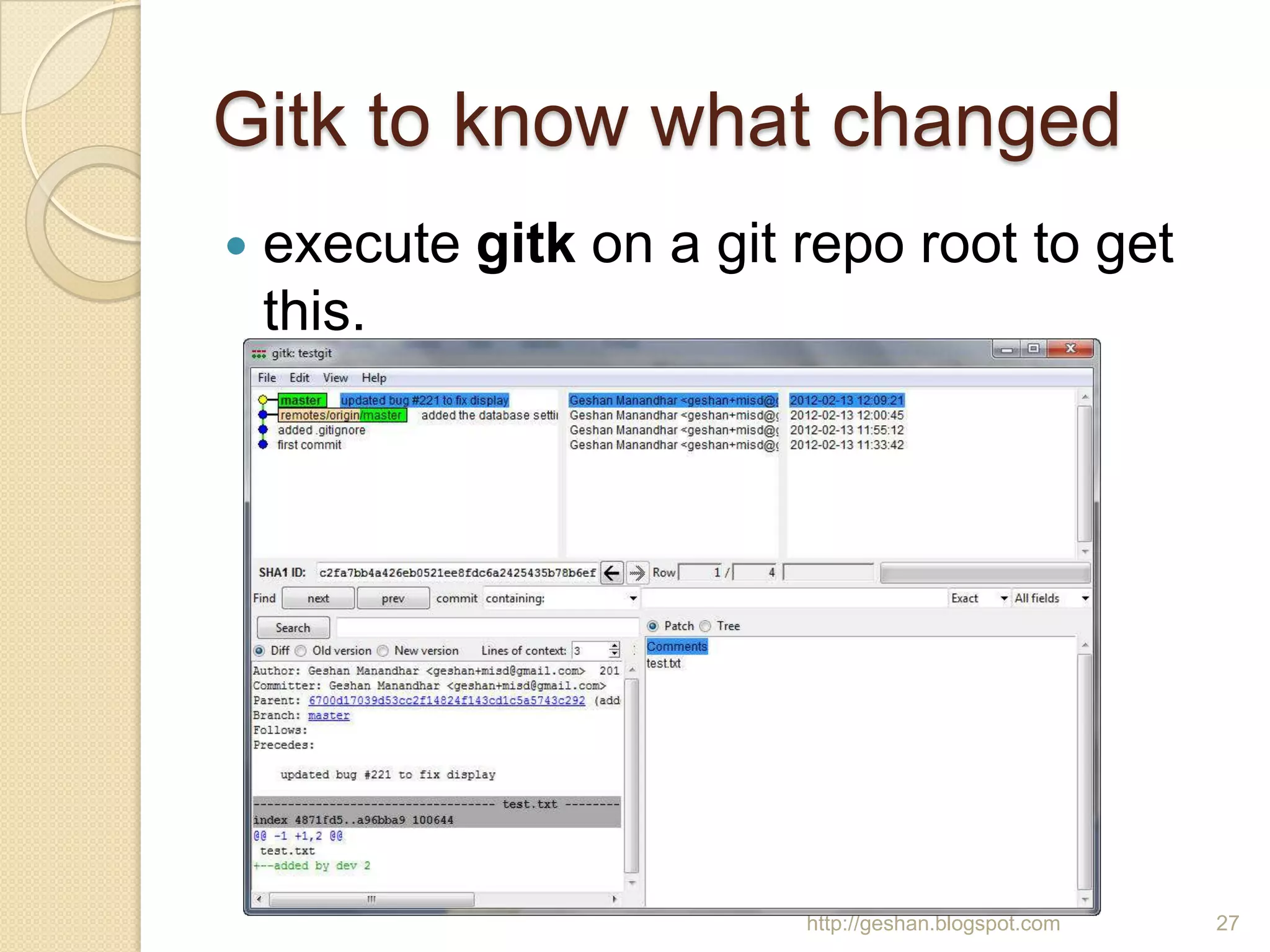
The document discusses how to use the Git version control system on Windows. It explains that Git is a free, open source distributed version control system used by many large projects. It then provides step-by-step instructions for installing Git on Windows using MsysGit, configuring user settings, initializing and preparing a working directory, making commits to a local repository, creating a public repository, pushing and pulling changes between the local and public repositories, using .gitignore files, and some common Git commands.